一、 实验目的
1 overview 包嗅探和欺骗是网络安全中的两个重要概念;它们是网络通信中的两大威胁。能够理解这两种威胁对于理解网络中的安全措施至关重要。有许多包嗅探和欺骗工具,如Wireshark、Tcpdump、Netwox等。其中一些工具被安全专家以及攻击者广泛使用。能够使用这些工具对学生来说很重要,但对于网络安全课程的学生来说,更重要的是了解这些工具是如何工作的,即包嗅探和欺骗是如何在软件中实现的。
本实验的目标是让学生掌握大多数嗅探和欺骗工具的基本技术。学生们将使用一些简单的嗅探和欺骗程序,阅读它们的源代码,修改它们,并最终对这些程序的技术方面有深入的了解。在本实验结束时,学生应该能够编写自己的嗅探和欺骗程序。
二、 实验步骤及结果
2 Environment Setup using Container
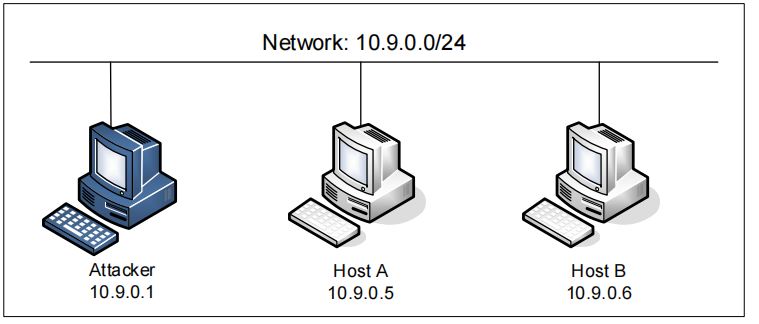
在这个实验室中,我们将使用三台连接到同一局域网的机器。我们可以使用三个虚拟机或三个容器。图1描述了使用容器进行的实验室环境设置。我们将对攻击者容器进行所有攻击,同时使用其他容器作为用户机器。
2.1 Container Setup and Commands 在labsetup文件夹下,启动docker
1 2 3 $ dcbuild $ dcup $ dcdown
要在容器上运行命令的话,我们通常需要在该容器上获取一个shell
我在这里先连接上docker
2.2 About the Attacker Container 在这个实验室中,攻击者需要能够嗅探包,但运行嗅探程序容器有问题,因为容器有效地连接到一个虚拟开关,所以它只能看到自己的流量,它永远不会看到其他容器中的数据包。为了解决这个问题,我们使用了攻击者容器的主机模式。这允许攻击者容器查看所有的流量。
3 Lab Task Set 1: Using Scapy to Sniff and Spoof Packets
3.1: Task 1.1: Sniffifing Packets
根据实验文档在/volumes下建立sniff.py
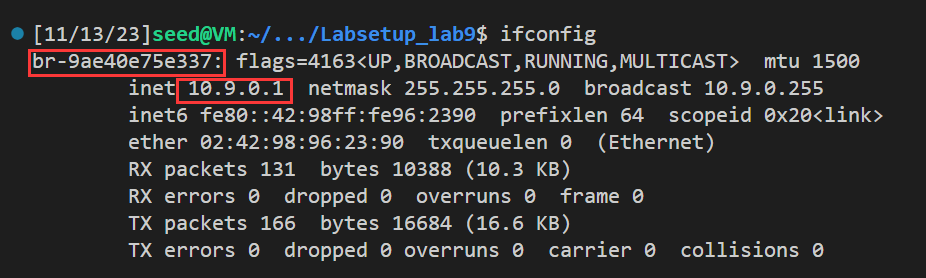
1 2 3 4 5 from scapy.all import *def print_pkt (pkt ): pkt.show() pkt = sniff(iface='br-9ae40e75e337' , filter ='icmp' , prn=print_pkt)
上面的代码将嗅出br-9ae40e75e337接口上的数据包。请阅读实验室设置部分中关于如何获取接口名称的说明。如果我们想嗅探多个接口,我们可以将所有接口放在一个列表中,并将其分配给iface。
Task 1.1A
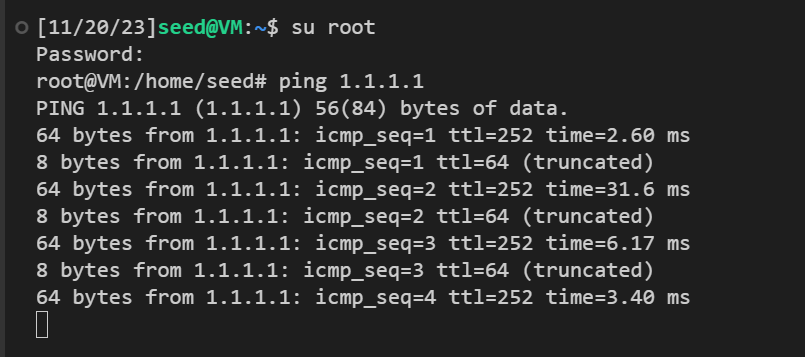
在上面的程序中,对于每个捕获的数据包,将调用回调函数打印pkt();这个函数将打印出有关数据包的一些信息。使用根权限运行该程序,并证明您确实可以捕获数据包。在此之后,再次运行该程序,但不使用根权限;描述和解释您的观察结果。
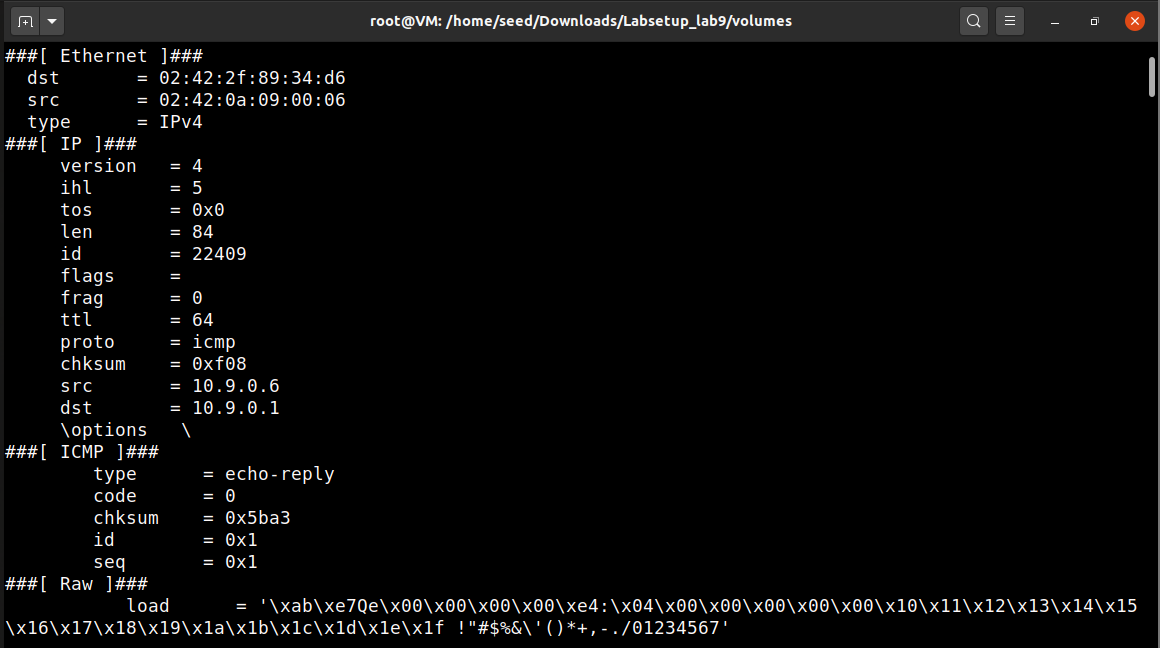
提前在HostA主机上ping 10.9.0.6,即可在Attacker主机上发现捕获的ICMP报文:
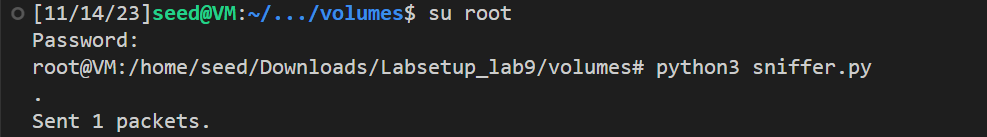
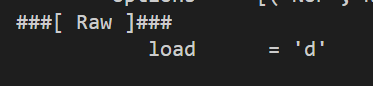
使用根权限运行该程序
可以看到我们嗅探到了以下内容:
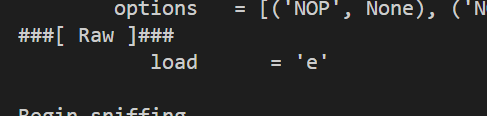
程序会反馈权限 错误!
Task 1.1B sniff函数中的filter控制程序会捕获的流量数据,
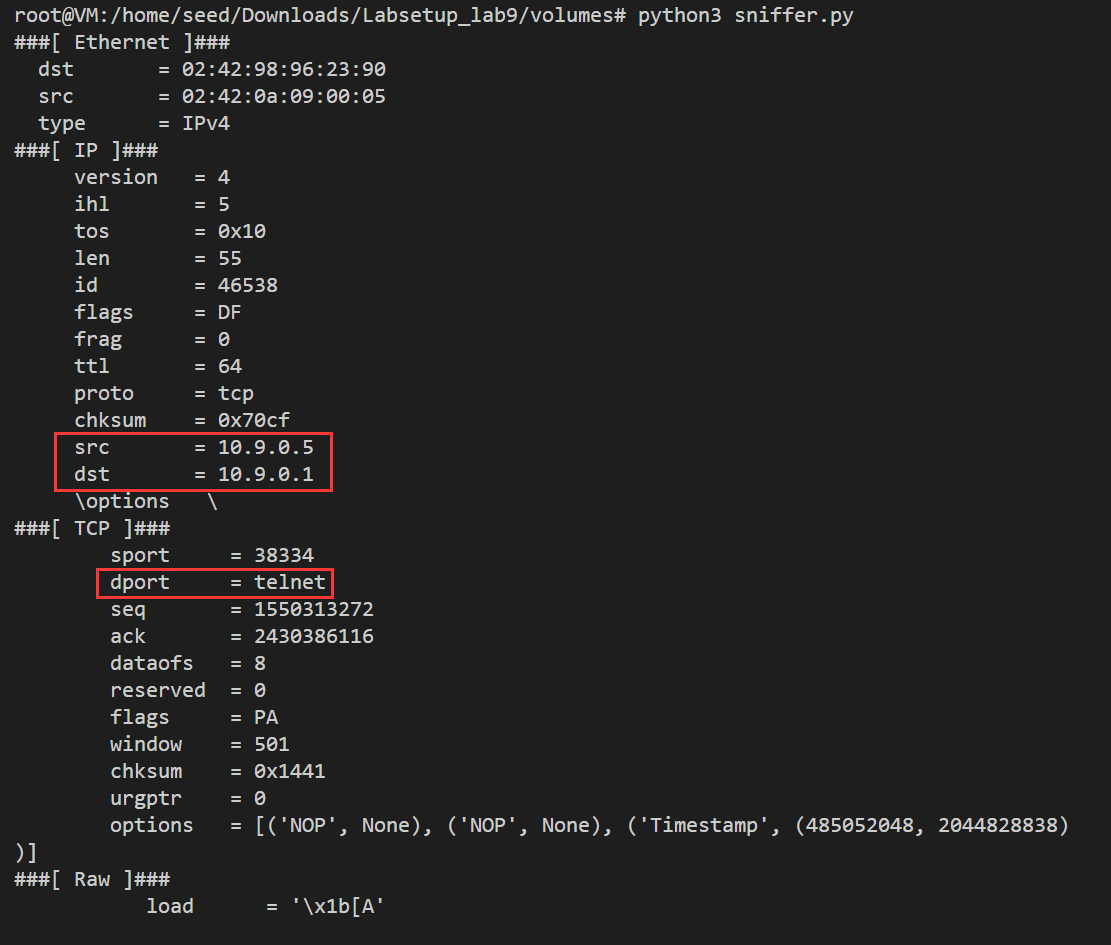
修改filter,使其只捕获来源IP为10.9.0.5,并且目的端口号为23的TCP数据
1 filter = 'tcp and ip src 10.9.0.5 and dst port 23'
目的端口23为telnet的专用端口号,在HostA上使用命令telnet 10.9.0.1发起请求,该请求将被捕获
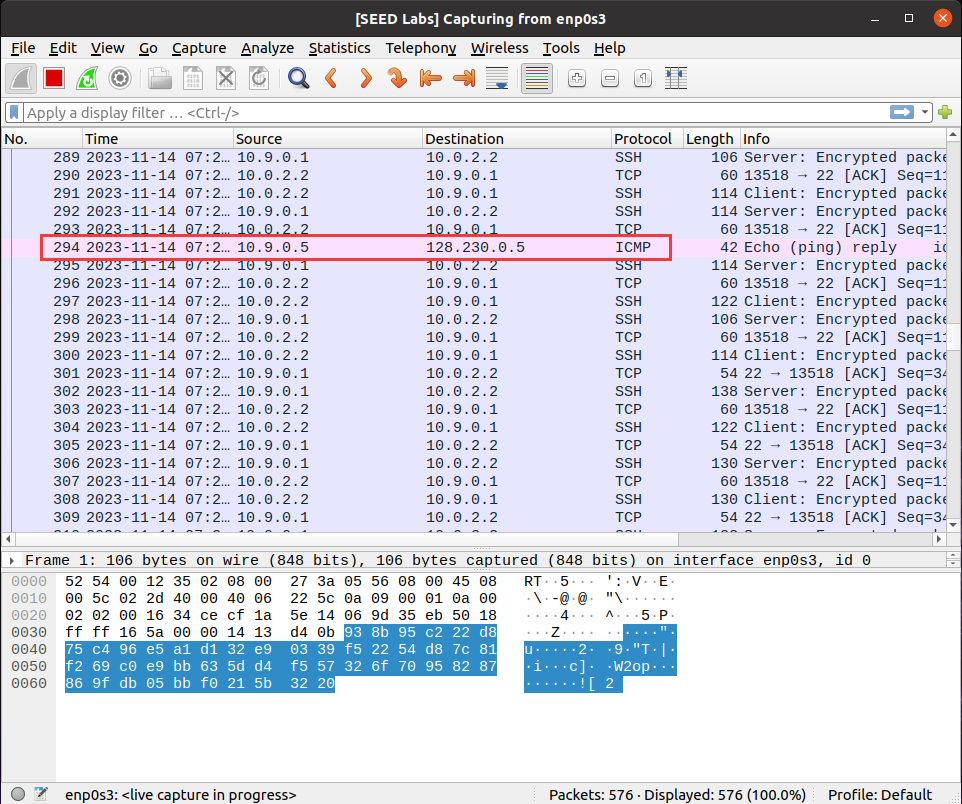
修改filter,使其能够拦截任何来自或发往子网128.230.0.0/16的流量
1 filter = 'net 128.230.0.0/16'
同样在HostA 上ping 128.230.0.5,无论该地址能否正常访问,都应该能够获取到对应的ICMP数据。(一定能收到ICMP请求报文)
3.2 Task 1.2: Spoofifing ICMP Packets
作为一个包欺骗工具,Scapy允许我们将IP包的字段设置为任意值。此任务的目的是用任意的源IP地址来欺骗IP数据包。我们将欺骗ICMP回波请求数据包,并将它们发送到同一网络上的另一个虚拟机。我们将使用线鲨来观察我们的请求是否会被接收人接受。如果被接受,将发送到欺骗的IP地址。
修改sniffer.py
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 from scapy.all import * ip = IP() ip.src = '128.230.0.5' ip.dst = '10.9.0.5' icmp = ICMP() send(ip/icmp)
运行该代码
3.3 Task 1.3: Traceroute
此任务的目标是使用Scapy来根据路由器的数量来估计VM和选定的目的地之间的距离。这基本上是由跟踪器工具实现的。在这个任务中,我们将编写我们自己的工具。这个想法非常简单:只需发送一个数据包(任何类型)到目的地,首先将它的实时时间(TTL)字段设置为1。这个数据包将被第一个路由器丢弃,它将向我们发送一个ICMP错误消息,告诉我们上线时间已经超过。这就是我们如何得到第一个路由器的IP地址。然后,我们将TTL字段增加到2,发送另一个数据包,并获得第二个路由器的IP地址。我们将重复这个过程,直到我们的数据包最终到达目的地。需要注意的是,这个实验只得到一个估计的结果,因为理论上,不是所有这些包采取相同的路径(但在实践中,它们可能在短时间内)。下面的代码显示了这个过程中的一轮代码。
修改sniffer.py
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 from scapy.all import * for i in range (1 ,30 ): a = IP() a.dst = '110.242.68.4' a.ttl = i b = ICMP() send(a/b)
在wireshark中开启监听网桥
3.4 Task 1.4: Sniffifing and-then Spoofifing
在此任务中,您将结合嗅探和欺骗技术来实现以下嗅探和欺骗程序。您需要在同一局域网上的两台机器:虚拟机和用户容器。从用户容器中,pingIPX。这将生成ICMP echo请求包。如果X是活动的,ping程序将收到一个回声响应,并打印出响应。你的嗅探-欺骗程序运行在VM上,它通过包嗅探监视局域网。当它看到ICMP echo请求时,无论目标IP地址是什么,您的程序应该立即使用包欺骗技术发送回声回复。因此,无论机器X是否活动,ping程序都将始终收到一个回复,表明X是活动的。您需要使用Scapy来完成此任务。在您的报告中,您需要提供证据来证明您的技术是有效的。
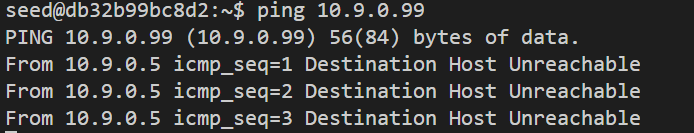
在被监听主机中ping 以下三个地址,发现只有第三个可以ping通
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 from scapy.all import * def spoof_pkt (pkt ): if ICMP in pkt and pkt[ICMP].type == 8 : print ("Original Packet......." ) print ("Source IP : " , pkt[IP].src) print ("Destination IP:" , pkt[IP].dst) ip = IP(src=pkt[IP].dst, dst=pkt[IP].src, ihl=pkt[IP].ihl) icmp = ICMP(type =0 , id =pkt[ICMP].id , seq=pkt[ICMP].seq) data = pkt[Raw].load newpkt = ip/icmp/data print ("Spoofed Packet......." ) print ("Source IP : " , newpkt[IP].src) print ("Destination IP : " , newpkt[IP].dst) send(newpkt, verbose=0 ) pkt = sniff(iface='br-9ae40e75e337' , filter ='icmp' , prn=spoof_pkt)
这段代码使用了Python的scapy库来操作网络数据包。它的主要目的是欺骗(spoof)ICMP数据包,即伪装数据包的源IP地址和目标IP地址。
4 Lab Task Set 2: Writing Programs to Sniff and Spoof Packets
4.1 Task 2.1: Writing Packet Sniffifing Program
使用pcap库可以很容易地编写嗅探器程序。使用pcap,嗅探器的任务变成了调用pcap库中的一个简单的过程序列。在序列的最后,一旦数据包被捕获,就将被放入缓冲区中进行进一步处理。数据包捕获的所有细节都由pcap库处理。
**Task 2.1A: Understanding How a Sniffer Works **
在这个任务中,学生需要编写一个嗅探程序来打印出每个捕获的数据包的源和目标IP地址。学生可以输入上面的代码或从种子书的网站上下载样本代码(https://www.handsonsecurity.net/figurecode.html)学生应该提供屏幕截图作为证据,以证明他们的嗅探程序能够成功运行,并产生预期的结果。
根据实验所给代码,完善代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 #include <pcap.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <arpa/inet.h> #define u_char unsigned char #define u_short unsigned short struct ethheader { u_char ether_dhost[6 ]; u_char ether_shost[6 ]; u_short ether_type; }; struct ipheader { unsigned char iph_ihl:4 , iph_ver:4 ; unsigned char iph_tos; unsigned short int iph_len; unsigned short int iph_ident; unsigned short int iph_flag:3 , iph_offset:13 ; unsigned char iph_ttl; unsigned char iph_protocol; unsigned short int iph_chksum; struct in_addr iph_sourceip ; struct in_addr iph_destip ; }; void got_packet (u_char *args, const struct pcap_pkthdr *header, const u_char *packet) { struct ethheader *eth =struct ethheader *)packet; if (ntohs(eth->ether_type) == 0x0800 ) { struct ipheader * ip =struct ipheader *) (packet + sizeof (struct ethheader)); printf (" From: %s\n" , inet_ntoa(ip->iph_sourceip)); printf (" To: %s\n" , inet_ntoa(ip->iph_destip)); switch (ip->iph_protocol) { case IPPROTO_TCP: printf (" Protocol: TCP\n\n" ); return ; case IPPROTO_UDP: printf (" Protocol: UDP\n\n" ); return ; case IPPROTO_ICMP: printf (" Protocol: ICMP\n\n" ); return ; default : printf (" Protocol: others\n\n" ); return ; } } } int main () { pcap_t *handle; char errbuf[PCAP_ERRBUF_SIZE]; struct bpf_program fp ; char filter_exp[] = "tcp and dst portrange 10-100" ; bpf_u_int32 net; handle = pcap_open_live("enp0s3" , BUFSIZ, 1 , 1000 , errbuf); printf ("listening on network card, ret: %p...\n" , handle); printf ("try to compile filter...\n" ); pcap_compile(handle, &fp, filter_exp, 0 , net); printf ("try to set filter...\n" ); pcap_setfilter(handle, &fp); printf ("start to sniff...\n" ); pcap_loop(handle, -1 , got_packet, NULL ); pcap_close(handle); return 0 ; }
这段代码通过使用libpcap库来捕获指定条件的网络数据包,并对捕获到的数据包进行解析和处理:
结构体定义:
ethheader:以太网头部结构体,包含了目标主机地址、源主机地址和协议类型等信息。
ipheader:IP数据包头部结构体,包含了IP版本、长度、源IP地址、目标IP地址等信息。
got_packet 函数:
这是一个回调函数,当捕获到一个数据包时被调用。
函数的参数解释:
args:用户传递的参数,这里没有使用。
header:捕获到的数据包的头部信息。
packet:捕获到的数据包的内容。
函数的功能:
通过解析数据包的以太网头部和IP头部,打印出源IP地址、目标IP地址和协议类型。
main 函数:
程序的入口函数。
主要步骤:
打开一个网络设备接口,准备开始捕获数据包。
编译并设置过滤器,只捕获目的端口在10到100之间的TCP数据包。
开始捕获数据包并调用 got_packet 函数进行处理。
循环捕获数据包直到程序结束。
关闭网络设备接口。
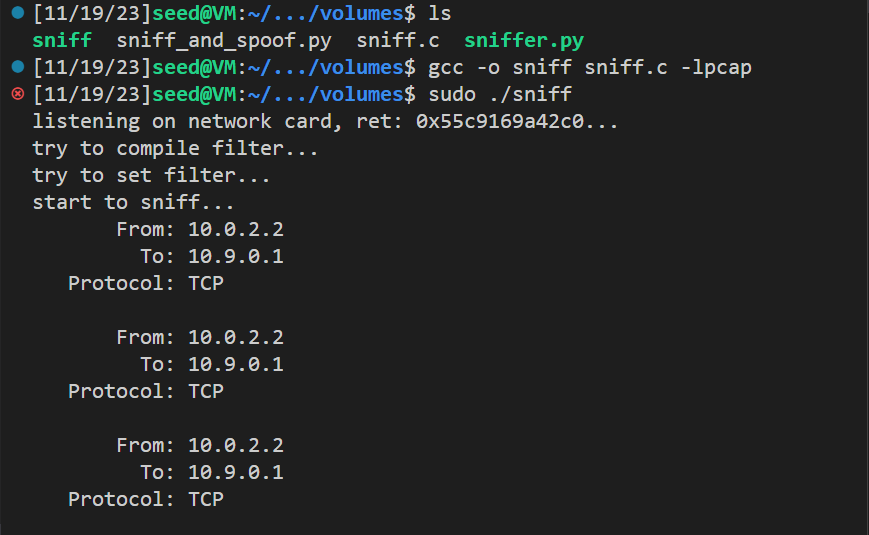
使用如下命令编译:
1 gcc -o sniff sniff.c -lpcap
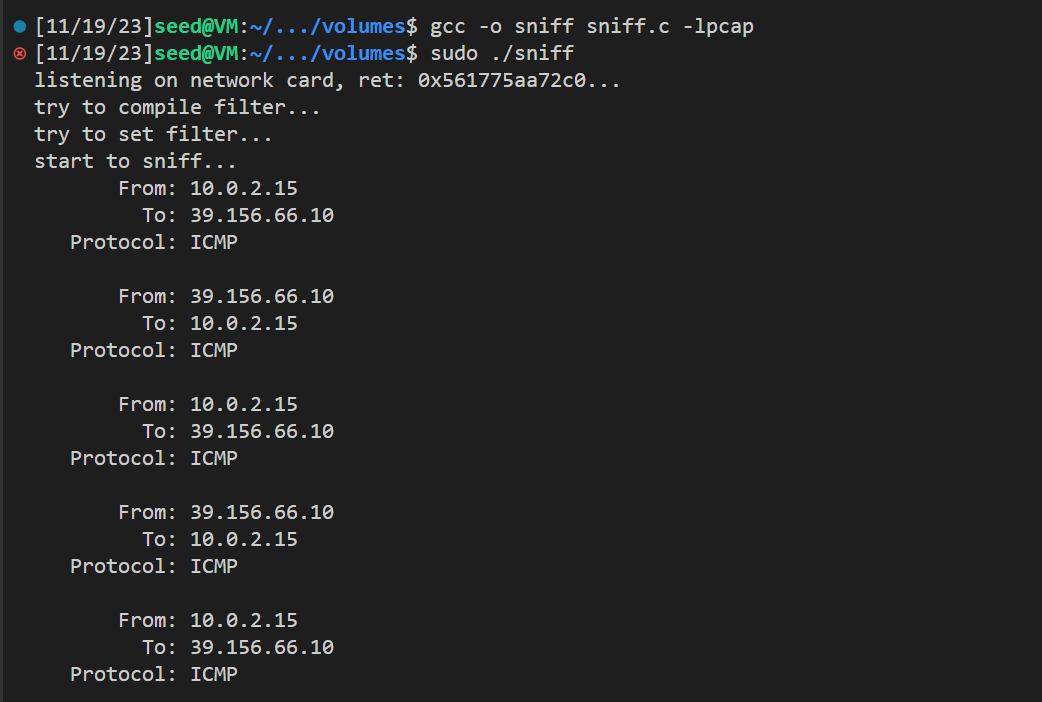
运行代码,可以看到发送的包出现在结果中:
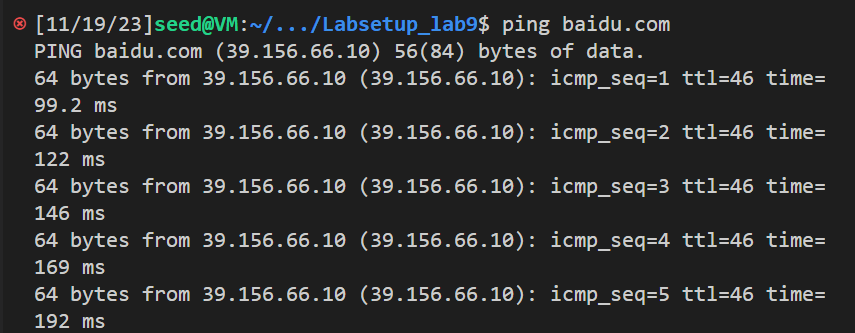
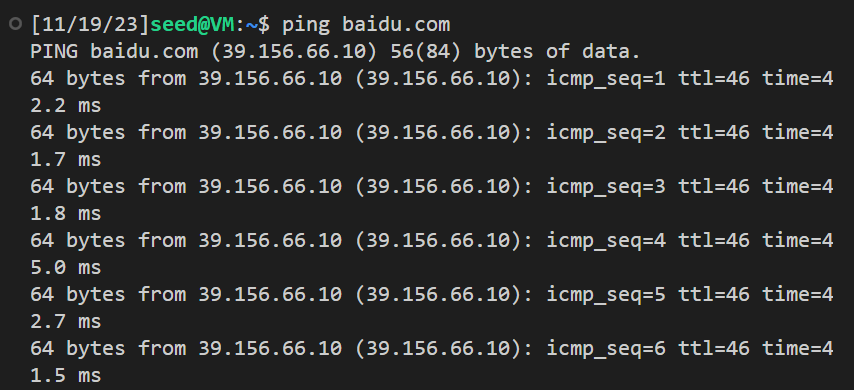
并尝试ping baidu.com:
Q1: 描述在你的嗅探程序中的库函数的调用
Q2: 为什么需要root权限才能运行嗅探程序?不使用root权限运行该程序会在哪里报错?
Q3: 打开嗅探程序的混杂模式。打开和关闭这个模式有什么区别?
Task 2.1B: Writing Filters
请为您的嗅探器程序编写过滤器表达式,以捕获以下每一个内容。你可以在网上找到关于pcap过滤器的手册。在实验室报告中,您需要包括屏幕截图来在应用这些过滤器后显示结果。
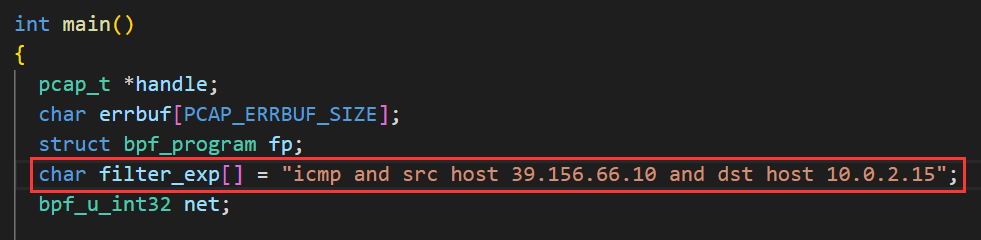
这部分还是复用 task 2.1A的代码,只是修改其中的过滤器而已。Pcap过滤器的例子
使用的过滤器为 icmp and src host 39.156.66.10 and dst host 10.0.2.15, 只捕捉从39.156.66.10(baidu的ip) 发送到 10.0.2.15的ICMP包
结果如下,可以看到全是从百度IP发送到 10.0.2.15的ICMP包,没有其他类型的包
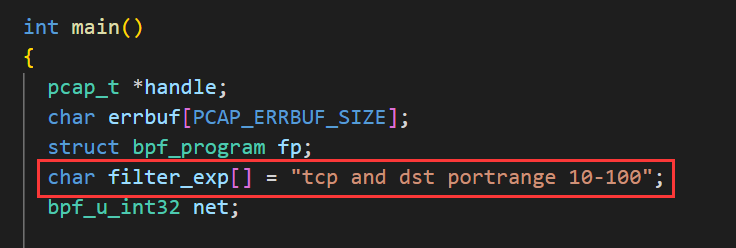
捕捉目的端口在10到100之间的TCP包:使用的过滤器为 tcp and dst portrange 10-100, 只捕捉TCP包
Task 2.1C: Sniffifing Passwords
请显示如何使用你的嗅探程序捕获密码时,有人使用网络,你正在监控。您可能需要修改嗅探器代码,以打印出捕获的TCP数据包的数据部分(telnet使用TCP)。如果您打印出整个数据部分,然后手动标记密码(或其部分密码)的位置,这是可以接受的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 from scapy.all import *print ("Begin sniffing..." )def print_pkt (pkt ): pkt.show() print (iface='br-9ae40e75e337' , sniff(filter ="tcp port 23" , prn=print_pkt))
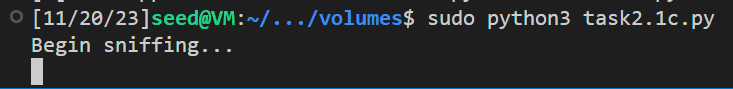
运行改代码:
1 sudo python3 task2.1 c.py
4.2 Task 2.2: Spoofifing
当普通用户发送数据包时,操作系统通常不允许用户设置协议头中的所有字段(如TCP、UDP和IP头)。操作系统将设置大部分字段,而只允许用户设置几个字段,如目标IP地址、目标端口号等。但是,如果用户具有根权限,那么他们可以在数据包头中设置任何任意字段。这被称为数据包欺骗,它可以通过原始套接字来完成。原始套接字为程序员提供了对包构造的绝对控制,允许程序员构造任意的包,包括设置头字段和有效负载。使用原始套接字非常简单;它涉及四个步骤: (1)创建一个原始套接字,(2)设置套接字选项,(3)构造数据包,以及(4)通过原始套接字发送数据包。有许多在线教程可以教你如何在C编程中使用原始套插字。我们已经将一些教程链接到该实验室的网页上。请阅读它们,并学习如何编写一个数据包欺骗程序。我们展示了这样一个程序的一个简单的框架。
Task 2.2A: Write a spoofifing program.
请用c编写您自己的数据包欺骗程序。您需要提供证据(例如,有线鲨鱼数据包跟踪),以表明您的程序成功地发送了欺骗的IP数据包。
这部分主要是伪造IP包。这里伪造是UDP包, 代码如下(spoof.c ):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 #include <unistd.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <sys/socket.h> #include <netinet/ip.h> #include <arpa/inet.h> #include "myheader.h" void send_raw_ip_packet (struct ipheader* ip) { struct sockaddr_in dest_info ; int enable = 1 ; int sock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_RAW, IPPROTO_RAW); printf ("sock: %d\n" , sock); setsockopt(sock, IPPROTO_IP, IP_HDRINCL, &enable, sizeof (enable)); dest_info.sin_family = AF_INET; dest_info.sin_addr = ip->iph_destip; sendto(sock, ip, ntohs(ip->iph_len), 0 , (struct sockaddr *)&dest_info, sizeof (dest_info)); close(sock); }
spoof_udp.c:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 #include <unistd.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <sys/socket.h> #include <netinet/ip.h> #include <arpa/inet.h> #include "myheader.h" void send_raw_ip_packet (struct ipheader* ip) ;int main () { char buffer[1500 ]; memset (buffer, 0 , 1500 ); struct ipheader *ip =struct ipheader *) buffer; struct udpheader *udp =struct udpheader *) (buffer + sizeof (struct ipheader)); char *data = buffer + sizeof (struct ipheader) + sizeof (struct udpheader); const char *msg = "Hello Server!\n" ; int data_len = strlen (msg); strncpy (data, msg, data_len); udp->udp_sport = htons(12345 ); udp->udp_dport = htons(9090 ); udp->udp_ulen = htons(sizeof (struct udpheader) + data_len); udp->udp_sum = 0 ; ip->iph_ver = 4 ; ip->iph_ihl = 5 ; ip->iph_ttl = 20 ; ip->iph_sourceip.s_addr = inet_addr("1.2.3.4" ); ip->iph_destip.s_addr = inet_addr("10.0.2.69" ); ip->iph_protocol = IPPROTO_UDP; ip->iph_len = htons(sizeof (struct ipheader) + sizeof (struct udpheader) + data_len); send_raw_ip_packet (ip); return 0 ; }
使用gcc -o spoof_udp spoof_udp.c spoof.c -lpcap 编译,sudo ./spoof_udp 运行,查看后台wireshark,可以看到我们伪造的UDP包
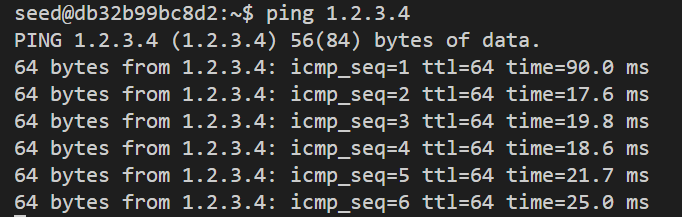
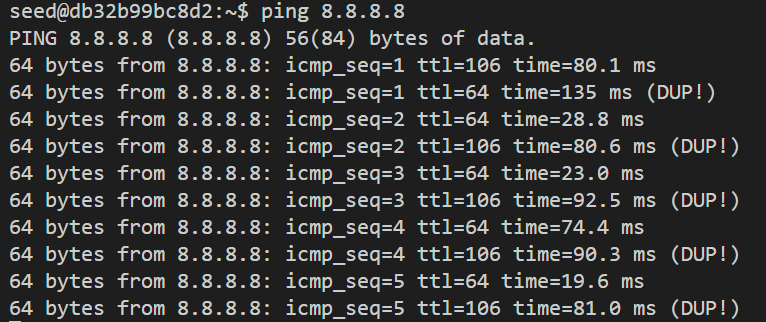
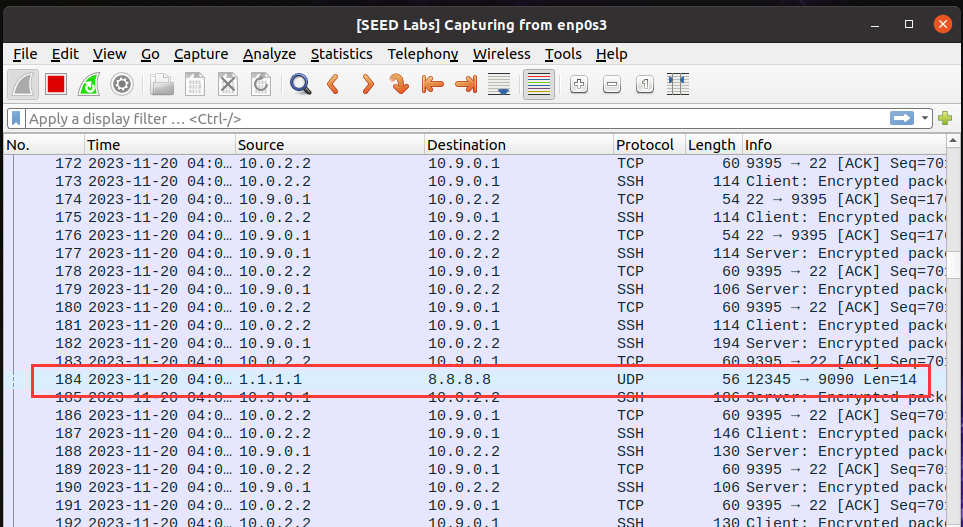
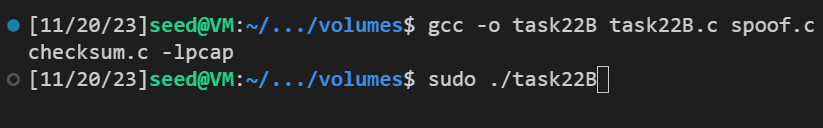
Task 2.2B: Spoof an ICMP Echo Request 这部分是伪造ICMP Echo请求。伪造的代码如下, 其中源IP10.9.0.5是局域网内另一个虚拟机的IP
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 #include <unistd.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <sys/socket.h> #include <netinet/ip.h> #include <arpa/inet.h> #include "myheader.h" unsigned short in_cksum (unsigned short *buf, int length) ;void send_raw_ip_packet (struct ipheader* ip) ;int main () { char buffer[1500 ]; memset (buffer, 0 , 1500 ); struct icmpheader *icmp =struct icmpheader *) (buffer + sizeof (struct ipheader)); icmp->icmp_type = 8 ; icmp->icmp_chksum = 0 ; icmp->icmp_chksum = in_cksum((unsigned short *)icmp, sizeof (struct icmpheader)); struct ipheader *ip =struct ipheader *) buffer; ip->iph_ver = 4 ; ip->iph_ihl = 5 ; ip->iph_ttl = 20 ; ip->iph_sourceip.s_addr = inet_addr("10.9.0.5" ); ip->iph_destip.s_addr = inet_addr("8.8.8.8" ); ip->iph_protocol = IPPROTO_ICMP; ip->iph_len = htons(sizeof (struct ipheader) + sizeof (struct icmpheader)); send_raw_ip_packet (ip); return 0 ; }
使用gcc -o task22B task22B.c spoof.c checksum.c -lpcap 进行编译, sudo ./task22B运行,查看后台的wireshark,如下:
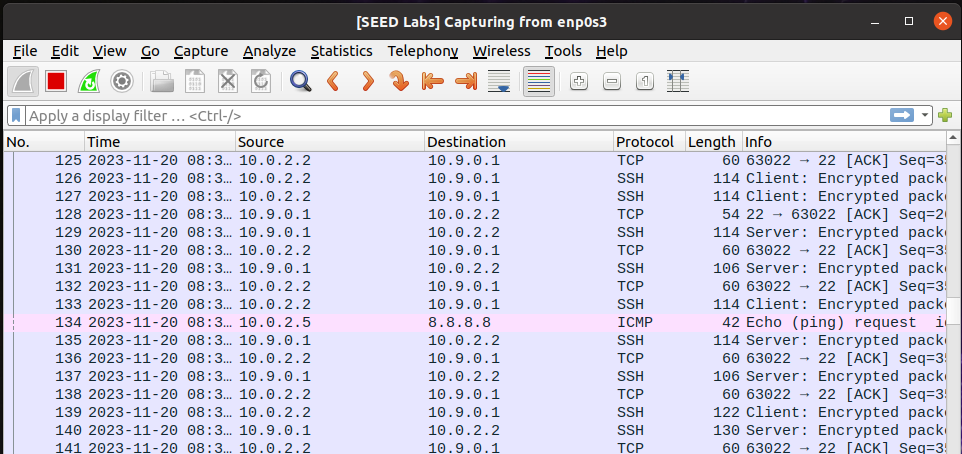
可以看到我们发送的源IP为10.0.2.5, 目的IP为8.8.8.8的ICMP包Q4: 是否可以将IP数据包长度字段设置为任意值,而不管实际的数据包有多大?
:::infoQ5: 使用原始套接字编程,是否需要计算IP报头的校验和?
:::infoQ6: 为什么您需要根权限来运行使用原始套接字的程序?如果没有根特权,程序在哪里失败 A6: Linux系统中,原始套接字访问是受限的,并且通常需要根权限(也称为超级用户权限)才能够访问。这是为了确保系统的安全性和防止滥用。原始套接字允许程序直接访问网络层数据包,包括IP头部和传输层协议头部。这种低级别的网络访问可以用于实现各种网络工具和协议,例如网络扫描器、数据包嗅探器和网络安全工具等。如果没有根权限,程序在尝试使用原始套接字时通常会失败。这是因为操作系统对访问原始套接字进行了限制,只有具有足够权限的用户才能够执行这些操作。如果没有特权,操作系统会拒绝相关系统调用,返回权限错误或类似的错误消息。
4.3 Task 2.3: Sniff and then Spoof
在此任务中,您将结合嗅探和欺骗技术来实现以下嗅探和欺骗程序。你需要在同一局域网上的两台机器。从机器A,你ping一个IP X。这将生成一个ICMP回波请求包。如果X是活动的,ping程序将收到一个回声响应,并打印出响应。你的嗅探和欺骗程序运行在攻击者的机器上,它通过数据包嗅探来监视局域网。当它看到ICMP echo请求时,无论目标IP地址是什么,您的程序应该立即使用包欺骗技术发送回声回复。因此,无论机器X是否活动,ping程序都将始终收到一个回复,表明X是活动的。您需要用C语言编写这样一个程序,并在报告中包含屏幕截图,以显示您的程序是工作的。请在您的报告中附上代码(有足够的内容)。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 #include <pcap.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <arpa/inet.h> #include "myheader.h" void got_packet (u_char *args, const struct pcap_pkthdr *header, const u_char *packet) { struct ethheader *eth =struct ethheader *)packet; if (ntohs(eth->ether_type) == 0x0800 ) { struct ipheader * ip =struct ipheader *) (packet + sizeof (struct ethheader)); printf ("From: %s " , inet_ntoa(ip->iph_sourceip)); printf ("To: %s " , inet_ntoa(ip->iph_destip)); if (ip->iph_protocol == IPPROTO_ICMP) printf ("protocal: ICMP\n" ); else printf ("protocal: Others\n" ); struct icmpheader *icmp_pkt =struct icmpheader *)(packet + sizeof (struct ethheader) + sizeof (struct ipheader)); if (ip->iph_protocol == IPPROTO_ICMP) { char buffer[1500 ]; memset (buffer, 0 , 1500 ); struct icmpheader *icmp =struct icmpheader *) (buffer + sizeof (struct ipheader)); icmp->icmp_type = 0 ; icmp->icmp_code = 0 ; icmp->icmp_id = icmp_pkt->icmp_id; icmp->icmp_seq = icmp_pkt->icmp_seq; printf ("icmp id: %d, seq: %d\n" , ntohs(icmp_pkt->icmp_id), ntohs(icmp_pkt->icmp_seq)); icmp->icmp_chksum = 0 ; icmp->icmp_chksum = in_cksum((unsigned short *)icmp, sizeof (struct icmpheader)); struct ipheader *ipp =struct ipheader *) buffer; ipp->iph_ver = 4 ; ipp->iph_ihl = 5 ; ipp->iph_ttl = 64 ; ipp->iph_sourceip.s_addr = ip->iph_destip.s_addr; ipp->iph_destip.s_addr = ip->iph_sourceip.s_addr; ipp->iph_protocol = IPPROTO_ICMP; ipp->iph_len = htons(sizeof (struct ipheader) + sizeof (struct icmpheader)); printf ("send tt source :%s\n" , inet_ntoa(ipp->iph_sourceip)); printf ("send tt dest: %s\n" , inet_ntoa(ipp->iph_destip)); send_raw_ip_packet (ipp); } } } int main () { pcap_t *handle; char errbuf[PCAP_ERRBUF_SIZE]; struct bpf_program fp ; char filter_exp[] = "icmp[icmptype]==icmp-echo" ; bpf_u_int32 net; handle = pcap_open_live("enp0s3" , BUFSIZ, 1 , 1000 , errbuf); printf ("listening on network card, ret: %p...\n" , handle); printf ("try to compile filter...\n" ); pcap_compile(handle, &fp, filter_exp, 0 , net); printf ("try to set filter...\n" ); pcap_setfilter(handle, &fp); printf ("start to sniff...\n" ); pcap_loop(handle, -1 , got_packet, NULL ); pcap_close(handle); return 0 ; }
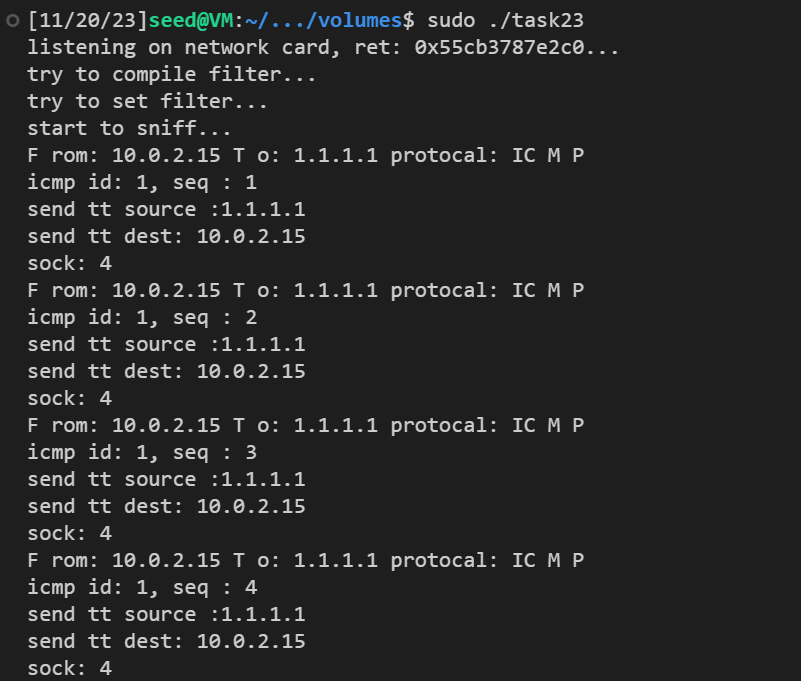
使用 gcc -o task23 task23.c checksum.c spoof.c -lpcap编译程序,sudo ./task23运行
程序输出如下: